
www.buildingsandcities.org/insights/news/occupant-surveys.html
What Have We Learnt from 20 Years of Occupant Surveys?
This peer-reviewed paper consolidates lessons from 20 years of post-occupancy surveys
Post-occupancy evaluation (POE) serves an important role in
collecting occupant insights on the performance of a building, understanding
flaws, and establishing ways to improve the indoor environment. Lindsay T. Graham,
Thomas Parkinson and Stefano Schiavon's recent Buildings & Cities
research paper LESSONS LEARNED FROM 20 YEARS OF CBE'S OCCUPANT SURVEY analyses
20 years of data to evaluate the structure and benchmarking metrics of the University
of California Berkeley Center for the Built Environment's (CBE) Occupant
Survey. Using data from over 90,000 respondents from approximately 900
buildings, they reassess whether occupant surveys are evaluating all they need
to, especially following the transformation that workspaces have experienced in
the last two decades.
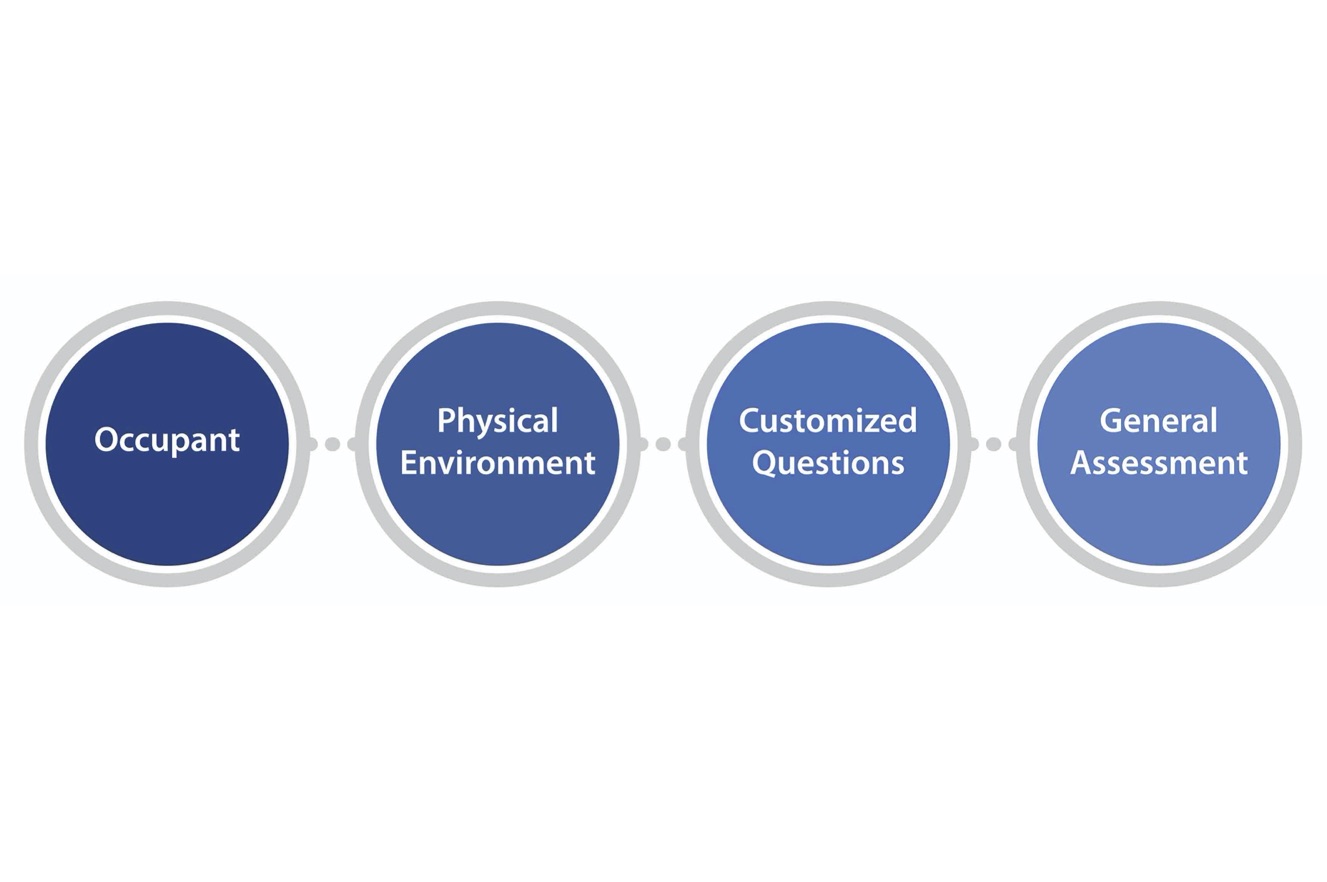
The general occupant survey structure includes:
- questions on the occupant themselves
- questions on their physical environment
- customized questions that occupants are directed to if they express some degree of dissatisfaction with aspects of their environment
- a general assessment of the overall environment.
Using correlation analysis, Principal Component Analysis and Hierarchical Clustering Analysis, the authors explore: the distribution of participant responses across several Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) factors; the structure and measurement properties of the survey; and how benchmarking metrics align with the tool's underlying structure.
Over the entire survey database, the authors find that roughly two thirds of respondents are satisfied with their workspace. Occupants are most satisfied with spaces' ease of interaction, amount of light, and space cleanliness; they are most dissatisfied with sound privacy, temperature, and noise level. In addition to aggregating findings, the authors use their analysis to reflect on the wider practice of POE and make recommendations for developing occupant surveys.
With regard to the survey structure, the authors make a case for streamlining questions. At present individual IEQ factors each have an associated question about whether they enhance or interfere with occupants' ability to complete their job. Instead, they suggest that it should be possible to have just one item that assesses the impact of the space overall on occupants' ability to complete tasks. In addition, the authors' correlation analysis suggests that multiple items around an IEQ theme are not always needed.
Crucially, the authors note that the occupant survey focuses on the problems and limitations within a space, rather than what is working well. They highlight that the survey offers an opportunity for insight into the successful elements of a design and suggest adding questions to capture this. Alongside this, questions that address occupant expectations of the space could be added to help understand the way space impacts emotions and could support occupants to achieve their tasks.
Cross-pollination between building science and social and health sciences could be especially fruitful. Specifically, they suggest incorporating well-developed and tested variables for stress, wellbeing and personality elements. This could be particularly fruitful for monitoring how comfortable people are in workspaces following the Covid-19 pandemic.
The use of workspaces is changing, particularly an increasing prevalence of agile work spaces. POE approaches need to adapt to this. The authors suggest generating shorter, experience-focused surveys utilising smartphones and wearable technologies. They also advocate for pairing this with monitoring of occupancy using sensors to gather a more holistic view of the occupant-building relationship.
The analysis presented in this paper is incredibly useful for truly understanding the utility of the tools that are used for monitoring our built environment such that they can be improved. Changes to the CBE Occupant Survey will be made as a result of this work.
Reference
Graham, L. T., Parkinson, T., & Schiavon, S. (2021). Lessons learned from 20 years of CBE's occupant surveys. Buildings and Cities, 2(1), pp. 166-184. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5334/bc.76
Latest Peer-Reviewed Journal Content
Living labs as ‘agents for change’ [editorial]
N Antaki, D Petrescu & V Marin
Post-disaster reconstruction: infill housing prototypes for Kathmandu
J Bolchover & K Mundle
Urban verticalisation: typologies of high-rise development in Santiago
D Moreno-Alba, C Marmolejo-Duarte, M Vicuña del Río & C Aguirre-Núñez
A public theatre as a living lab to create resilience
A Apostu & M Drăghici
Reconstruction in post-war Rome: transnational flows and national identity
J Jiang
Reframing disaster recovery through spatial justice: an integrated framework
M A Gasseloğlu & J E Gonçalves
Tracking energy signatures of British homes from 2020 to 2025
C Hanmer, J Few, F Hollick, S Elam & T Oreszczyn
Spatial (in)justice shaping the home as a space of work
D Milián Bernal, J Laitinen, H Shevchenko, O Ivanova, S Pelsmakers & E Nisonen
Working at home: tactics to reappropriate the home
D Milián Bernal, S Pelsmakers, E Nisonen & J Vanhatalo
Living labs and building testing labs: enabling climate change adaptation
J Hugo & M Farhadian
Energy sufficiency, space temperature and public policy
J Morley
Living labs: a systematic review of success parameters and outcomes
J M Müller
Towards a universal framework for heat pump monitoring at scale
J Crawley, L Domoney, A O’Donovan, J Wingfield, C Dinu, O Kinnane, P O’Sullivan
Living knowledge labs: creating community and inclusive nature-based solutions
J L Fernández-Pacheco Sáez, I Rasskin-Gutman, N Martín-Bermúdez, A Pérez-Del-Campo
A living lab approach to co-designing climate adaptation strategies
M K Barati & S Bankaru-Swamy
Mediation roles and ecologies within resilience-focused urban living labs
N Antaki, D Petrescu, M Schalk, E Brandao, D Calciu & V Marin
Negotiating expertise in Nepal’s post-earthquake disaster reconstruction
K Rankin, M Suji, B Pandey, J Baniya, D V Hirslund, B Limbu, N Rawal & S Shneiderman
Designing for pro-environmental behaviour change: the aspiration–reality gap
J Simpson & J Uttley
Lifetimes of demolished buildings in US and European cities
J Berglund-Brown, I Dobie, J Hewitt, C De Wolf & J Ochsendorf
Expanding the framework of urban living labs using grassroots methods
T Ahmed, I Delsante & L Migliavacca
Youth engagement in urban living labs: tools, methods and pedagogies
N Charalambous, C Panayi, C Mady, T Augustinčić & D Berc
Co-creating urban transformation: a stakeholder analysis for Germany’s heat transition
P Heger, C Bieber, M Hendawy & A Shooshtari
Placemaking living lab: creating resilient social and spatial infrastructures
M Dodd, N Madabhushi & R Lees
Church pipe organs: historical tuning records as indoor environmental evidence
B Bingley, A Knight & Y Xing
A framework for 1.5°C-aligned GHG budgets in architecture
G Betti, I Spaar, D Bachmann, A Jerosch-Herold, E Kühner, R Yang, K Avhad & S Sinning
Net zero retrofit of the building stock [editorial]
D Godoy-Shimizu & P Steadman
Co-learning in living labs: nurturing civic agency and resilience
A Belfield
Join Our Community

The most important part of any journal is our people – readers, authors, reviewers, editorial board members and editors. You are cordially invited to join our community by joining our mailing list. We send out occasional emails about the journal – calls for papers, special issues, events and more.
We will not share your email with third parties. Read more


Latest Commentaries
COP30 Report
Matti Kuittinen (Aalto University) reflects on his experience of attending the 2025 UN Conference of the Parties in Belém, Brazil. The roadmaps and commitments failed to deliver the objectives of the 2025 Paris Agreement. However, 2 countries - Japan and Senegal - announced they are creating roadmaps to decarbonise their buildings. An international group of government ministers put housing on the agenda - specifying the need for reduced carbon and energy use along with affordability, quality and climate resilience.
Building-Related Research: New Context, New Challenges
Raymond J. Cole (University of British Columbia) reflects on the key challenges raised in the 34 commissioned essays for Buildings & Cities 5th anniversary. Not only are key research issues identified, but the consequences of changing contexts for conducting research and tailoring its influence on society are highlighted as key areas of action.