
www.buildingsandcities.org/insights/news/energy-policy-urban-ghg.html
Impacts of Energy Policy on Urban GHG Emissions

Which combination of policy measures are most appropriate for reducing urban emissions? New peer-reviewed research shows how economic, technology and urban building energy models can be combined and used to evaluate policy efficacy.
Until now, uncertainties of
economic and market-driven factors in urban building energy models (UBEM) have
been a challenge for building energy modellers. The spatial impact of energy
and emissions policies in urban environments is often hard to determine. UBEMs
often fail to recognise the financial and social influences over new buildings
and/ or retrofitting existing building stocks. In INTEGRATION OF AN ENERGY-ECONOMY MODEL WITH AN URBAN ENERGY MODEL, Lu et al. present a new
approach for integrating these different types of model. Specifically, the
authors integrate outputs from a spatial economic model with a spatially
explicit community-level UBEM. This is a major contribution in the development
of an integrated modelling approach, but also in quantifying the co-benefits of
multi-scale effects of energy and emission reduction policies.
Lu et al. adopt a 'sandbox' approach to simulate urban form and building retrofit policies, working at a neighbourhood scale. The sandbox represents a particular urban form, including population density, street pattern, block size and land-use proportions, all derived from a real neighbourhood. This allows for an increasingly realistic representation of the integrated processes that influence energy-usage and emissions output, including fuel choice, building design, mechanical systems, urban form and behaviour.
With this combination, the researchers have been able to model the evolution of a neighbourhood's individual buildings (HVAC system and the building shell) over time. This provides a much higher level of granularity than many existing efforts to understand how building stock changes over time in response to different policy strategies. The interaction between building technology policies and different urban growth-management strategies can be better understood and harnessed. Policy makers are afforded extremely valuable and detailed insights into the impact of energy policies at an individual building-level, prior to their implementation. Insights arising from this combined model will assist practitioners involved in both city planning and energy management.
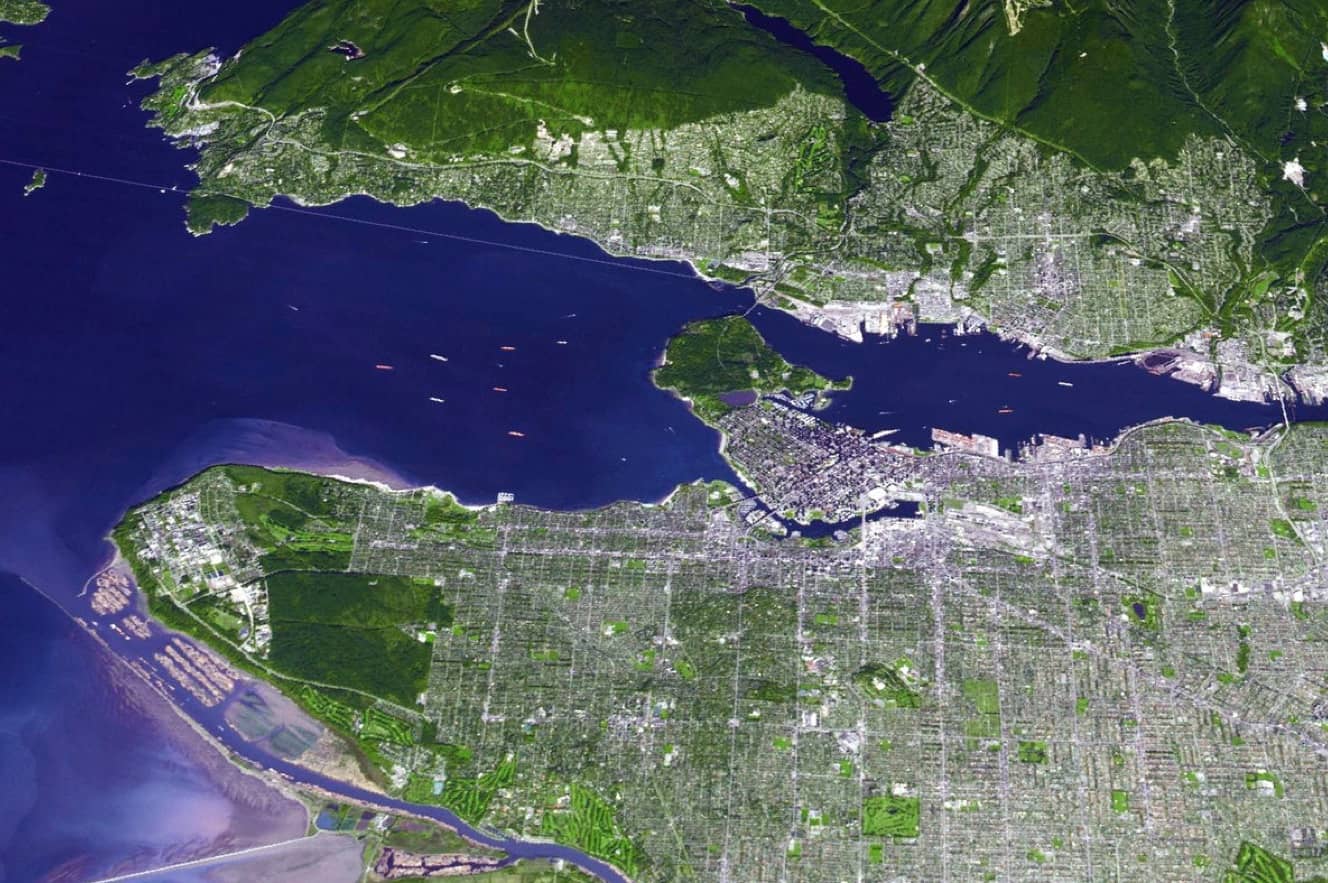
A case study applies the model to the Sunset region of Vancouver, Canada. The case study explored three urban-form policy experiments: dispersed, commercial corridor, and transportation-oriented development (TOD). The analysis illustrates the combined results of a technology policy regulating a shift towards electrification and a spatial urban form densification policy. The authors identify specific growth-management strategies that can be more effective for reducing emissions than when integrated with other urban form strategies.
Policies focused on energy
and emissions standards for new buildings will be relatively more effective in
areas with a growth-management strategy that necessitates the redevelopment of
many existing buildings. This demonstrates a useful approach for understanding
exactly which policy instruments, such as densification, higher building energy
standards, and fuel switching, will bring the most emissions reductions.
Funding
The research was funded by Pacific Institute for Climate Solutions (PICS). Additional funding from Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI) Canada and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) supported tool development and related research.
Reference
Lu, Y., Scott, A., Kim, J. C., Curi, C. B., McCarty, J., Pardy, A., Rysanek, A., Girling, C & Kellett, R. (2021). Integration of an energy-economy model with an urban energy model. Buildings and Cities, 2(1), 114-133. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5334/bc.71Latest Peer-Reviewed Journal Content
Energy sufficiency, space temperature and public policy
J Morley
Living labs: a systematic review of success parameters and outcomes
J M Müller
Towards a universal framework for heat pump monitoring at scale
J Crawley, L Domoney, A O’Donovan, J Wingfield, C Dinu, O Kinnane, P O’Sullivan
Living knowledge labs: creating community and inclusive nature-based solutions
J L Fernández-Pacheco Sáez, I Rasskin-Gutman, N Martín-Bermúdez, A Pérez-Del-Campo
A living lab approach to co-designing climate adaptation strategies
M K Barati & S Bankaru-Swamy
Mediation roles and ecologies within resilience-focused urban living labs
N Antaki, D Petrescu, M Schalk, E Brandao, D Calciu & V Marin
Negotiating expertise in Nepal’s post-earthquake disaster reconstruction
K Rankin, M Suji, B Pandey, J Baniya, D V Hirslund, B Limbu, N Rawal & S Shneiderman
Designing for pro-environmental behaviour change: the aspiration–reality gap
J Simpson & J Uttley
Lifetimes of demolished buildings in US and European cities
J Berglund-Brown, I Dobie, J Hewitt, C De Wolf & J Ochsendorf
Expanding the framework of urban living labs using grassroots methods
T Ahmed, I Delsante & L Migliavacca
Youth engagement in urban living labs: tools, methods and pedagogies
N Charalambous, C Panayi, C Mady, T Augustinčić & D Berc
Co-creating urban transformation: a stakeholder analysis for Germany’s heat transition
P Heger, C Bieber, M Hendawy & A Shooshtari
Placemaking living lab: creating resilient social and spatial infrastructures
M Dodd, N Madabhushi & R Lees
Church pipe organs: historical tuning records as indoor environmental evidence
B Bingley, A Knight & Y Xing
A framework for 1.5°C-aligned GHG budgets in architecture
G Betti, I Spaar, D Bachmann, A Jerosch-Herold, E Kühner, R Yang, K Avhad & S Sinning
Net zero retrofit of the building stock [editorial]
D Godoy-Shimizu & P Steadman
Co-learning in living labs: nurturing civic agency and resilience
A Belfield
The importance of multi-roles and code-switching in living labs
H Noller & A Tarik
Researchers’ shifting roles in living labs for knowledge co-production
C-C Dobre & G Faldi
Increasing civic resilience in urban living labs: city authorities’ roles
E Alatalo, M Laine & M Kyrönviita
Co-curation as civic practice in community engagement
Z Li, M Sunikka-Blank, R Purohit & F Samuel
Preserving buildings: emission reductions from circular economy strategies in Austria
N Alaux, V Kulmer, J Vogel & A Passer
Urban living labs: relationality between institutions and local circularity
P Palo, M Adelfio, J Lundin & E Brandão
Living labs: epistemic modelling, temporariness and land value
J Clossick, T Khonsari & U Steven
Co-creating interventions to prevent mosquito-borne disease transmission in hospitals
O Sloan Wood, E Lupenza, D M Agnello, J B Knudsen, M Msellem, K L Schiøler & F Saleh
Circularity at the neighbourhood scale: co-creative living lab lessons
J Honsa, A Versele, T Van de Kerckhove & C Piccardo
Positive energy districts and energy communities: how living labs create value
E Malakhatka, O Shafqat, A Sandoff & L Thuvander
Built environment governance and professionalism: the end of laissez-faire (again)
S Foxell
Co-creating justice in housing energy transitions through energy living labs
D Ricci, C Leiwakabessy, S van Wieringen, P de Koning & T Konstantinou
HVAC characterisation of existing Canadian buildings for decarbonisation retrofit identification
J Adebisi & J J McArthur
Simulation and the building performance gap [editorial]
M Donn
Developing criteria for effective building-sector commitments in nationally determined contributions
P Graham, K McFarlane & M Taheri
Join Our Community

The most important part of any journal is our people – readers, authors, reviewers, editorial board members and editors. You are cordially invited to join our community by joining our mailing list. We send out occasional emails about the journal – calls for papers, special issues, events and more.
We will not share your email with third parties. Read more


Latest Commentaries
COP30 Report
Matti Kuittinen (Aalto University) reflects on his experience of attending the 2025 UN Conference of the Parties in Belém, Brazil. The roadmaps and commitments failed to deliver the objectives of the 2025 Paris Agreement. However, 2 countries - Japan and Senegal - announced they are creating roadmaps to decarbonise their buildings. An international group of government ministers put housing on the agenda - specifying the need for reduced carbon and energy use along with affordability, quality and climate resilience.
Building-Related Research: New Context, New Challenges
Raymond J. Cole (University of British Columbia) reflects on the key challenges raised in the 34 commissioned essays for Buildings & Cities 5th anniversary. Not only are key research issues identified, but the consequences of changing contexts for conducting research and tailoring its influence on society are highlighted as key areas of action.